Interference
1.) It is due to the superposition of two or more than two wavefronts coming from coherent sources.
2.) The intensity of all bright fringes are same
3.) Interference fringes either of the same size or decrease after moving away from the center.
4.) Dark fringes are usually perfectly dark.
5.) A minimum coherent source is needed.
Diffraction:
1.) It occurs due to secondary wavelets, originating from infinite different points of the same wavefronts.
2.) Central maxima of bright fringe is followed by either side maxima of decreasing intensity.
3.) Interference fringes are never of the same shape and size.
4.) Dark fringes are not perfectly dark.
5.) It is possible by either one or more than one source which need not be coherent.
Superconductors and its properties
Superconductivity
The property of a substance in which the electrical resistance of the substance is zero at very low temperatures. This property of substance is called superconductivity.
For certain substances, like mercury, the resistivity suddenly drops to zero at very low temperatures typically near the boiling point of liquid helium. Some metals, doped semiconductors, alloys and ceramics (i.e. these are insulators at room temperature and superconduct at higher temperatures than the metals) show superconductivity.
Temperature Dependence of Resistivity
In superconducting substances, the resistivity suddenly drops to zero at a particular temperature known as critical temperature ($T_{c}$) or
transition temperature and remains zero below that as shown in Figure below.
The critical temperature for mercury is $4.2 K$. Below this critical temperature, mercury is superconducting whereas above this temperature it behaves like a normal conductor. Different superconducting materials have different critical temperatures but the nature of the variation in resistivity with temperature remains more or less similar.
Properties of Superconductors
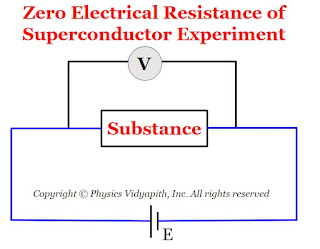
1.) Zero electrical resistance:
The electrical resistivity of superconductors is zero at very low temperatures. The experimental testing of zero resistance was tried by
connecting the substance at room temperature to a battery. A voltmeter was connected across the specimen to measure the electric potential difference across the specimen as shown in Figure below.
As the temperature of the substance gets lowered. It was observed that below a particular temperature (i.e. critical temperature), the electric potential difference across the substance suddenly dropped to zero.
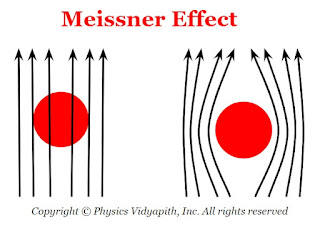
2) Meissner effect:
When a substance is placed in a weak magnetic field and cooled below the critical temperature then this substance behaves like perfect diamagnets with zero magnetic induction. This phenomenon is called the Meissner effect.
The magnetic induction inside the substance in the normal state is given by, Superconductors
$B = \mu_{\circ} (H +M)$
where $H$ is the externally applied magnetic field and $M$ is the magnetization inside the substance.
When the temperature $T$ of the specimen is lowered below its critical temperature
$B= 0$
$M_{\circ}(H + M) = 0$
$H = - M$
The susceptibility $\chi$ is given by,
$\chi=\frac{M}{H}$
For diamagnetic substance $\chi=-1$
As the relative permeability
$\mu_{r}=1+\chi$
$\therefore \mu_{r}=0$
This indicates perfect diamagnetism.
Meissner effect cannot be explained by assuming that the superconductor is a perfect conductor with zero electrical conductivity. The electric field is given by,
$E=\frac{V}{l}$
$E=\frac{iR}{l}$
$E=\frac{iR}{l} \frac{A}{A}$
$E=\frac{RA}{l} \frac{i}{A}$
$E=\rho J$
Where
$\rho$ = Resistivity
$J$= Current density
If $\rho$ becomes zero for a finite current density $J$, then $E =0$.
From Maxwell's equations,
$\nabla \times \overrightarrow{E} = \frac{d \overrightarrow{B}}{dt}$
As $E=0$, $\frac{d \overrightarrow{B}}{dt} =0$
$\therefore \overrightarrow{B} = Constant$
$\therefore$ In a conductor the flux cannot change on cooling below the critical temperature. This contradicts the Meissner effects according to which the flux must reduce to zero and hence superconductor is not just a perfect conductor.
Due to the Meissner effect, superconductors strongly repel external magnets which leads to magnetic levitation.
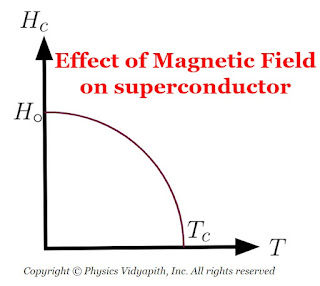
3) Effect of magnetic field on superconductors :
Superconductivity is destroyed by sufficiently strong magnetic fields. The minimum value of the applied magnetic field required to destroy
superconductivity is called the critical field $H_{c}$. and is a function of temperature. Above the critical temperature $T_{c}$, $H_{c} = 0$. Below the critical temperature, the variation of $H_{c}$, with temperature $T$ is as shown in Figure below and be represented by the equation
$H_{c}=H_{\circ} \left[ 1- \left(\frac{T}{T_{c}}\right) \right]$
where $H_{\circ}$ is the critical field at absolute zero.
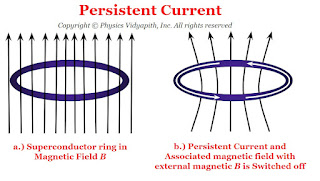
4) Persistent currents :
When a ring is placed in the magnetic field and the field is switched off, a current is induced in the ring. This induced current is called the persistent current.
The magnitude of current remains constant even though there is no source of e.m.f. as the resistance of the superconducting ring is zero. These currents flowing in the ring produce magnetic fields that do not require any power supply to maintain a constant field.
5) Isotope effect :
According to observations, the critical temperature of superconductors varies with isotopic mass. The critical temperature is smaller for larger isotopic mass. This phenomenon is called the isotope effect.
The relation between critical temperature $T_{c}$ and isotopic mass $M$ is given by,
$T_{c}M^{a} = Constant$
For most of the materials $a =\frac{1}{2}$
$\therefore T_{c}M^{\frac{1}{2}} = Constant$
$\therefore T_{c} \propto M^{-\frac{1}{2}} $
As lattice vibrations are reduced for larger isotopic masses, the isotope effect indicates that superconductivity is due to the interaction between electrons and lattice vibrations.
6) Critical Current:
All the current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. Similarly, When current flows through a superconducting wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. If the current in the superconducting wire is increased, the magnetic field intensity just outside it will increase and reach the critical field $H_{c}$. If the current is increased beyond this value, the wire will be subjected to a magnetic field exceeding the critical field due to which the superconducting state will be destroyed and then it will revert to its normal state. The maximum current that a superconductor can carry without reverting back to its normal state is known as critical current.
The magnetic induction due to a wire of radius $r$ just outside it is
$B=\frac{\mu_{\circ}i}{2 \pi r}$
$\mu_{\circ} H=\frac{\mu_{\circ}i}{2 \pi r}$
$H=\frac{i}{2 \pi r}$
If the critical current in $_{c}$, and critical field is $H_{c}$, ,
$H_{c}=\frac{i_{c}}{2 \pi r}$
$i_{c}=2 \pi r H_{c}$
Types of Superconductors
There are two types of superconductors based on the difference in magnetization exhibited by them. These are known as Type-I (or soft) and Type-II (or hard) superconductors.
1) Type-I Superconductors (Soft superconductors):
The magnetization curve for a Type-I -M superconductor is shown in Figure below. Type-I superconductors show the complete Meissner effect when the applied magnetic field H is less than the critical field $H_{c}$.
The magnetization in the superconductor is proportional to the applied field and the superconductors behave like perfect diamagnet.
For $H > H_{ç}$, the magnetization is negligible and the superconductor becomes a normal conductor. Pure elements show such magnetization curves. The values of $H_{c}$, are very low.
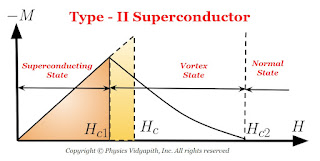
2) Type-II Superconductors (Hard superconductors)
The magnetization curve for a type-II superconductor is shown in Figure below.
There are two critical field $H_{c1}$ and $H_{c2}$ in Type-II superconductors that characterize it. Upto the lower critical field $H_{c1}$, the superconductor is perfectly diamagnetic and flux is completely ejected out from the superconductor. The magnetization in the superconductor is proportional to the applied field. Between $H_{c1}$ and $H_{c2}$, the Meissner effect is incomplete but electrically it is a superconductor but not magnetically. This state is called the mixed state or the vortex state.
The values of $H_{c}$ may be $100$ times or higher than the critical field $H_{c}$, for type-I superconductors.
Above the higher critical field $H_{c2}$ the superconductor becomes a normal conductor.
Type-II superconductors are usually alloys or transition metals with high values of electrical resistivity in the normal state.
High-Temperature Superconductors
Kamerlingh Onnes discovered superconductivity in mercury in 1911 with a critical temperature of $4.2 K$. The research was then focussed on materials with larger critical temperatures so that the phenomenon could become commercially viable.
But, till about 1986, the highest critical temperatures were observed to be nearly $20 K$. In 1986, an oxide of lanthanum, barium, and copper ($La_{1.85} Ba_{0.15} CuO_{4}$) was observed to have a critical temperature of $36 K$. In 1987, an oxide of yttrium, barium and copper ($YBa_{2}Cu_{3},0_{7}$) was found to have a critical temperature of $90 K$ and then an oxide of thallium, barium, calcium and copper($Tl_{2}Ba_{2}Ca_{2}Cu_{3}O_{10}$) was found to have a critical temperature of $120 K$.
The presence of parallel sheets of $CuO_{2}$ is the main feature of high-temperature superconductors.. Efforts are going on to find superconductors with critical temperatures near room temperature.
$J$= Current density
Kinetic Theory of Ideal Gases
German scientists R.Classius and J.C. Maxwell had propounded the kinetic theory of gases. According to this model, every gas is made up of very fine particles called molecules. All
the molecules of a gas are similar in all properties. We know that $ 1 cm^{3}$ of water is heated at $100^{\circ}C$ temperature, producing $1$ atmosphere pressure $1671 cm$ of water vapour. From this, it is known that the volume actually occupied by the molecules in $1671 cm^{3}$
of water vapour is only $1 cm^{3}$, and the remaining $1670 cm^{3}$ of volume is empty. In other words, in the gaseous state of matter, there is a lot of free space between the molecules. This fact is true for all gases. The molecules of gases are always moving randomly in all possible directions. During motion, these molecules collide with each other and with the walls of
the vessel in which the gas is kept. After each collision, both the direction and speed of motion of these molecules keep changing.
All collisions between molecules and molecules or between molecules and the walls are elastic. This implies that total kinetic energy and momentum are conserved.
Assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases
There are the following assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases.
1. The molecules of a gas are very small, rigid, spherical and completely elastic. The volume of the molecules is the volume in which the gas is present, is negligible compared to the volume of the gas.
2. Although the molecules of a gas can move with every possible velocity in every direction, but the number of molecules per unit volume or molecular density remains the same.
3. There is no force of attraction or repulsion between the molecules, as a result of which they do not have potential energy; their entire energy is kinetic energy.
4. When the molecules of a gas come very close to each other, there is a repulsive force between them, due to which their speed and direction of motion change.
This phenomenon is called a 'collision' between two molecules. Between two consecutive collisions, the molecules move in a straight line with a constant speed. The distance travelled by the molecule between two consecutive collisions is called the free path and its average is called the mean free path.
5. The mutual collision between the molecules and the collision between the molecule and the wall is perfectly elastic, that is, the kinetic energy of the molecules is conserved.
6 The time of collision between the molecules is negligible compared to the distance travelled freely by the molecule.
7. Since the amount of molecules is negligible and the velocity is high, therefore there is no effect of gravity on the motion of the molecules.
Newton's Corpuscular Model
Newton's Corpuscular Theory
In the year 1675, Newton proposed the corpuscular theory of light to explain the existing phenomenon of light. There are the following assumptions of this theory:
1. The light consists of very small, lightweight, and invisible particles. These particles are known as corpuscles.
2. These corpuscles move with the velocity of light in a homogeneous medium in all possible directions in a straight line and they carry kinetic energy with them.
3. When these corpuscles fall on the retina of the eye, they produce the sensation of vision.
4. The size of corpuscles of different colors is different (ie, the color of light depends on the size of the corpuscle).
(A) Success of Carpuscles Theory
Based on this theory, the following facts related to light were explained successfully:
1. The light has energy: Since corpuscles have kinetic energy. Therefore, the energy of the light beam is due to the kinetic energy of the corpuscles.
2. Motion of light along a straight line: Since velocity of the corpuscle is very high, the effect of external forces on it is
negligible. Therefore, it moves in a straight line.
3. Motion of light in vacuum: Corpuscles can move through vacuum.
4. Reflection of light: To explain the reflection of light, Newton assumed that when a corpuscle reaches close to a reflecting surface, then the surface repels it with a force whose direction is perpendicular to the surface and whose magnitude decreases sharply as the distance of corpuscles increases from the surface.
In Figure, let $PO$ be a reflecting surface and $P'Q'$ be an imaginary surface just above it at negligible height. When a light corpuscle moves towards the surface, then it moves along a straight line from $A$ to $B$ (since the force is zero). As it reaches the point $B$ of surface $PQ$, a repulsive force starts acting perpendicular to the surface (upward in the figure). Let $i$ is an angle of incidence at point $B$, then the velocity of the corpuscles at point $B$ has two components- component parallel to surface $V_{||} =v \: sin \: i$ and component perpendicular to surface $V_{|} = v \: cos \: i$. After crossing point $B$, the parallel component remains same but the perpendicular component decreases. At point $C$ of surface $PQ$, the perpendicular component becomes zero. After this direction of the perpendicular component changes and the corpuscles move along path CD. Beyond D again it moves along a straight line as the force becomes ineffective. If $r$ is the angle of reflection at point $D$, then the parallel component of velocity at $D$ will be $v\: sin\: r$. Since the parallel component remains constant. Therefore, comparing them at points $B$ and $D$.
$v \: sin \: i=v \: sin\: r$
$sin \: i= sin\: r$
$i=r$
i.e., the above equation shows that the incident angle and the reflected angle are equal. In the figure above, incident ray, reflected ray and normal all three are in the plane of paper. Therefore laws of reflection are verified.
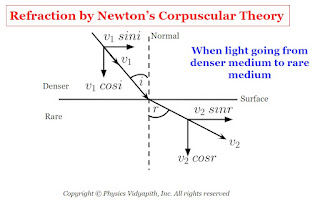
5. Refraction of light: To explain the refraction of light, Newton considered two different situations :
a.) When the light goes from a denser medium to a rare medium: In this condition when the corpuscle reaches near the surface, the surface exerts a normal repulsive force on it. As a result, the perpendicular component of velocity of the corpuscles decreases however it does not reduce to zero as in the case of refraction. Therefore, enters the second medium with a reduced perpendicular component and same constant value of the parallel component i.e., moves along a straight line bending away from normal.
If $i$ and $r$ are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction and $v_{1}$ and $v_{2}$ are the velocity of corpuscle in medium first and second medium. If the parallel component is constant,
$v_{1} \: sin \: i =v_{2} \: sin\: r$
$\frac{sin \: i}{sinr} =\frac{v_{2}}{v_{1}}$
From Figure
$i \lt r$
Therefore
$sin \: i \lt sin\: r$
$v_{2} \lt v_{1}$
Therefore, from the corpuscular theory, velocity light in a denser medium ($v_{1}$) is greater than the velocity light in a rare medium ($v_{2}$).
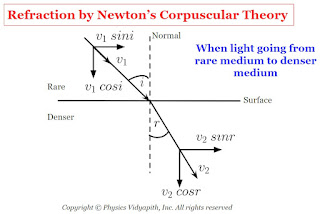
b.) When the light goes from a rare medium to a denser medium: In this condition when the corpuscle reaches near to the surface, the surface attracts it normally. As a result, the normal component of its velocity increases. Therefore, the corpuscular enters the second medium with an increased normal component and the same parallel component of velocity and moves along a straight line bending towards the normal.
$v_{1} \: sin \: i =v_{2} \: sin\: r$
$\frac{sin \: i}{sinr} =\frac{v_{2}}{v_{1}}$
From Figure
$i \gt r$
Therefore
$ sin \: i \gt sin\: r$
$v_{2} \gt v_{1}$
Therefore, velocity light in a denser medium ($v_{1}$) is greater than the velocity light in a rare medium ($v_{2}$).
B) Failure of the Corpuscles Theory
The following are the main reasons for the failure of this theory:
1. Interference, diffraction, polarisation of light, and the photoelectric effect, etc. can not be explained using this principle. For example, in interference, when two light beams interfere, darkness is produced at the same places. It is not possible that two corpuscles destroy each other.
2. According to this theory, the velocity of light is greater in the denser medium as compared to the rare medium. But Focault's had proved experimentally that the velocity of light is less in denser mediums as compared to the velocity of light in rare mediums.
3. According to this theory, greater the temperature of the source greater the velocity of the corpuscles. Actually, the velocity of light does not depend on the temperature of the source.
4. According to this theory, the mass of the source should decrease as it continuously emits corpuscles but it does not happen in reality.
5. In this theory two opposite assumptions are considered to explain reflection and refraction. To explain reflection and refraction through denser to rarer, the repulsive force by the surface is assumed and to explain refraction from rare to denser, the force of attraction by the surface is assumed. These assumptions are opposite and they don't have any scientific base.
Popular Posts
-
Let $S$ be a point monochromatic source of light of wavelength $\lambda$ placed at the focus of collimating lens $L_{1}$. The light beam is ...
-
Angle of Acceptance → "If incident angle of light on the core for which the incident angle on the core-cladding interface equals t...
-
Derivation of interference of light due to a wedge-shaped thin film: Interference of light due to wedge-shaped thin film The wedge...
-
Maxwell's Equations: Maxwell's equation of the electromagnetic wave is a collection of four equations i.e. Gauss's law of elec...
-
Let a plane wavefront be incident normally on slit $S_{1}$ and $S_{2}$ of equal $e$ and separated by an opaque distance $d$.The diffracted l...
Study-Material
Categories
Alternating Current Circuits
(10)
Atomic and Molecular Physics
(4)
Biomedical
(1)
Capacitors
(6)
Classical Mechanics
(12)
Current carrying loop in magnetic field
(5)
Current Electricity
(10)
Dielectric Materials
(1)
Electromagnetic Induction
(3)
Electromagnetic Wave Theory
(23)
Electrostatic
(22)
Energy Science and Engineering
(2)
Error and Measurement
(2)
Gravitation
(11)
Heat and Thermodynamics
(3)
Kinematics Theory Of Gases
(2)
Laser System & Application
(15)
Magnetic Effect of Current
(9)
Magnetic Substances
(3)
Mechanical Properties of Fluids
(4)
Nanoscience & Nanotechnology
(4)
Nuclear Physics
(7)
Numerical Problems and Solutions
(2)
Optical Fibre
(5)
Optics
(25)
Photoelectric Effect
(3)
Quantum Mechanics
(34)
Relativity
(8)
Semiconductors
(2)
Superconductors
(1)
Topic wise MCQ
(9)
Units and Dimensions
(1)
Waves
(5)