Let a plane wavefront be incident normally on slit $S_{1}$ and $S_{2}$ of equal $e$ and separated by an opaque distance $d$.The diffracted light is focused on the screen $XY$. The diffracted pattern on the screen consists of equally spaced bright and dark fringe due to interference of light from both the slits and modulated by diffraction pattern from individual slits.
op
The diffraction pattern due to double-slit can be explained considering the following points →
All the points in slits $S_{1}$ and $S_{2}$ will send secondary waves in all directions.
All the secondary waves moving along the incident wave will be focussed at $P$ and the diffracted waves will be focussed at $P'$
The amplitude at $P'$ is the resultant from two slit each of amplitude $R=\frac{A\:sin\alpha}{\alpha}$
T two waves from two-slit $S_{1}$ and $S_{2}$ will interfere at $P'$
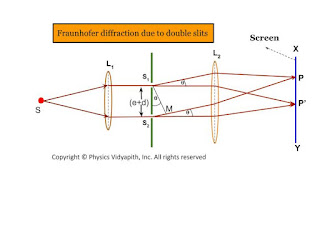 |
| Fraunhofer diffraction due to double slits |
Expression for Intensity →
$\Delta = S_{2}M$
$\Delta=(e+d)sin\theta\qquad(1)$
The corresponding phase difference →
$\Delta\phi= \frac{2\pi}{\lambda}(e+d)sin\theta \qquad(2)$
Let $\Delta \phi =2 \beta \qquad(3)$
$\beta=\frac{\pi}{\lambda}(e+d)sin\theta\qquad(4)$
The resultant amplitude at $P'$ can be obtained by the vector addition method. The resultant amplitude at $P'$
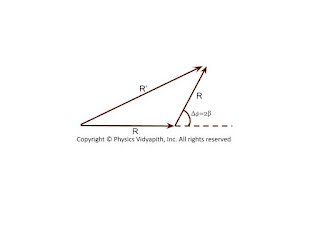 |
| Resultant Vector |
$R'^{2}=R^{2}+R^{2}+2R.R.cos\Delta\phi$
$R'^{2}=R^{2}+R^{2}+2R.R.cos2\beta$ {\qquad $\because 2\beta=\Delta\phi$}
$R'^{2}=2R^{2}+2R^{2}cos2\beta$
$R'^{2}=2R^{2} \left( 1+cos2\beta \right)$
$R'^{2}=4R^{2} cos^{2}\beta \qquad(5)$
Where $R$ - Resultant amplitude of each slit $S_{1}$
$R=\frac{A\: sin\alpha}{\alpha} \qquad(6)$
Substituting the value of $R$ in equation $(5)$
$R'^{2}=4 A^{2} \frac{sin^{2}\alpha}{\alpha^{2}} cos^{2} \beta \qquad(7)$
$R'=2 A \frac{sin\alpha}{\alpha} cos\beta \qquad(8)$
The intensity of the resultant diffraction pattern at $P'$
$I=4 A^{2} \frac{sin^{2}\alpha}{\alpha^{2}} cos^{2} \beta \qquad(9)$
Where $\alpha=\frac{\pi}{\lambda}e\:sin\theta \qquad(10)$
The resultant intensity at any point is the contribution of the following two factors →
The factor $\frac{A^{2}sin^{2}\alpha}{\alpha^{2}}$, represents the intensity distribution due to diffraction from any individual slits.
The factor $cos^{2}\beta$ represents the intensity distribution due to interference of waves from two parallel slits.
Condition for Maxima and Minima →
- Maxima and minima due to diffraction term
- Maxima and minima due to interference term
1. Maxima and minima due to diffraction term →
i.) Principal Maxima →
The diffraction term $\frac{A^{2}sin^{2}\alpha}{\alpha^{2}}$ gives the central maxima, for $\alpha=0$ so
$\frac{\pi}{\lambda}e\: sin\theta=0$
$sin\theta =0 $
$\theta=0$
ii.) Minima →
The diffraction term $\frac{A^{2}sin^{2}\alpha}{\alpha^{2}}$ gives the central minima, for $sin\alpha=0$ so
$\alpha=\pm m\pi$
$e\:sin\theta=\pm m\pi$
iii.) Secondary Maxima →
The secondary maxima are obtained in the direction given by →
$\alpha= \pm\frac{3\pi}{2},\pm\frac{5\pi}{2},\pm\frac{7\pi}{2},..............$
2. Maxima and minima due to interference term →
i.) Maxima→
The interference term $cos^{2}\beta$ gives maxima in the direction →
$cos^{2}=1$
$\beta=\pm n \pi$
$\frac{\pi}{\lambda}(e+d)sin\theta= \pm n \pi$
$(e+d)sin\theta= \pm n \lambda$
Where $n=0,1,2,3,.....$
In the direction $\theta=0^{\circ}$, the principle maxima due to interference and diffraction coincide.
ii.) Minima→
The interference term $cos^{2}\beta$ gives minima in the direction →
$cos^{2}\beta=0$
$\beta=\pm(2n+1)\frac{\pi}{2}$
$(e+d)sin\theta=\pm(2n+1)\frac{\pi}{2}$
The intensity distribution curve due to the diffraction term, interference term, and the combined effect is shown in the figure below →
 |
| Intensity diagram of Fraunhofer double slit Experiment |





