Gauss's Law:
Gauss's law for electric flux is given by
Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1813. He extended the work of
Joseph-Louis Lagrange. This formula was first formulated in 1713 by Lagrange. Gauss's law stated that:
The electric flux passing normal through any closed hypothetical surface is always equal to the $\frac{1}{\epsilon_{0}}$ times of the total charge enclosed within that closed surface. This closed hypothetical surface is known as Gaussian surface.
Let us consider that a $+q$ coulomb charge is enclosed within the Gaussian's surface. Then according to Gauss's Law, the electric flux will be:
$\phi _{E}= \frac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
The electric flux of the electric field →
$\phi_{E}=\oint \overrightarrow{E}\cdot\overrightarrow{dA}$
Substitute this value of electric flux $\phi_{E}$ in the above formula so we get →
$\oint \overrightarrow{E}\cdot\overrightarrow{dA}=\frac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
Where $\epsilon_{0}$ → Permittivity of the free space
The above formula of Gauss's law is applicable only under the following two conditions:
1.) The electric field at every point on the surface is either perpendicular or tangential.
2.) The magnitude of the electric field at every point where it is perpendicular to the surface has a constant value.
Derivation of Gauss's law from Coulomb's law:
1.) When the charge is within the surface
2.) When the charge is outside the surface
1. When the charge is within the surface:
Let a charge $+q$ is placed at point $O$ within a closed surface of irregular shape. Consider a point $P$ on the surface which is at a distance $r$ from the point $O$. Now take a small element or area $\overrightarrow{dA}$ around the point $P$. If $\theta$ is the angle between $\overrightarrow{E}$ and $\overrightarrow{dA}$ then electric flux through small element or area $\overrightarrow{dA}$
$d\phi_{E}=\overrightarrow{E}\cdot\overrightarrow{dA}$
$d\phi_{E}=E\:dA\:cos\theta \qquad\quad\quad (1)$
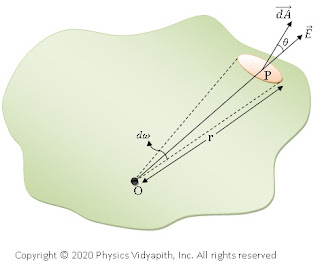 |
| When charge is inside the surface |
According to Coulomb's law, the electric field intensity $E$ at point $P$.
$E=\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}\frac{q}{r^{2}}$
Now substitute the value of electric field intensity $E$ in equation $(1)$
$d\phi_{E}=\frac{q}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}\frac{dA\:cos\theta}{r^{2}}$
but $\frac{dA\:cos\theta}{r^{2}}$ is the solid angle $d\omega$ subtended by $dA$ at point $O$. Hence the above equation can be written as
$d\phi_{E}=\frac{q}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}d\omega$
So, The total flux $\phi_{E}$ over the entire surface can be found by integrating the above equation
$\oint d\phi_{E}= \frac{q}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}\oint d\omega$
For entire surface solid angle $d\omega$ will be equal to $4\pi$ i.e. $d\omega=4\pi$
$\phi _{E}= \frac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
If the closed surface enclosed with several charges like $q_{1},q_{2},q_{3},.....-q_{1},-q_{2},-q_{3},.....$. Now each charge will contribute to the total electric flux $\phi_{E}$.
$\phi_{E}= \frac{1}{\epsilon_{0}}\left [ q_{1}+q_{2}+q_{3}...-q_{1}-q_{2}-q_{3}... \right ]$
Here $\quad q=q_{i}-q_{j}$
$\phi_{E}= \frac{1}{\epsilon_{0}}\sum_{i=1,j=1}^{n}(q_{i}-q_{j})$
$\phi_{E}= \frac{1}{\epsilon_{0}}\sum q$
Where $\sum q$ → Algebraic Sum of all the charges
2. When the charge is outside the surface:
Let a point charge $+q$ be situated at point $O$ outside the closed surface. Now a cone of solid angle $d\omega$ from point $O$ cuts the surface area $dA_{1}$, $dA_{2}$ at point $P$ and $Q$ respectively. The electric flux for an outward normal is positive while for inward normal is negative so
The electric flux at point $P$ through an area
$d\phi_{1}$= $-\left (\frac{q}{4\pi \epsilon_{0}} \right )d\omega$
The electric flux at point $Q$ through area
$d\phi_{2}$= $+\left (\frac{q}{4\pi \epsilon_{0}} \right )d\omega$
The Total electric flux will be sum of all the electric flux passing through areas of surface →
$\phi_{E}=d\phi_{1}+d\phi_{2}$
$\phi_{E}=-\left ( \frac{q}{4\pi \epsilon_{0}} \right )d\omega+\left ( \frac{q}{4\pi \epsilon_{0}} \right )d\omega $
$\phi_{E}=0$
The above equation is true for all cones from point $O$ through any surface, however irregular it may be-
The total electric flux over the entire surface due to an external charge is zero.
This verifies Gauss's law.
Application of Gauss's law:
There are following some important application given below:
- Electric field intensity due to a point charge
- Electric field intensity due to uniformly charged spherical Shell (for Thin and Thick)
- Electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged solid sphere (Conducting and Non-conducting)
- Electric field intensity due to uniformly charged infinite plane sheet (for Thin and Thick)
- Electric field intensity due to uniformly charged parallel sheet
- Electric field intensity due to charged infinite length wire






