Introduction:
The prefix 'nano' means a billionth ($10^{-9}$). The field of nanotechnology is the study of various structures of matter having dimensions of the order of a billionth of a meter. These particles are called nanoparticles. Nanotechnology is based on the fact that particles that are smaller than about $100 nm$ give rise to new properties of nanostructures built from them.
Particles that are smaller than the characteristic length for a particular phenomenon show different physical and chemical properties than particles of larger sizes. For example, mechanical properties, optical properties, conductivity, melting point, and reactivity have all been observed to change when particles become smaller than the characteristic length.
Gold and silver nanoparticles were used in window glass panes to obtain a variety of beautiful colors. Nanotechnology has a wide range of applications like producing lighter but stronger materials, constructing faster switches for computers, improving drug delivery to specific organs of the body, etc.
The radii of atoms and most of the molecules are less than a nanometer. Nanoparticles are generally considered to have a radius in the range of $1 nm$ to $100 nm$ which can have $25$ to $10^{6}$ atoms. A cluster of $1 nm$ radius has approximately $25$ atoms. This definition of nanoparticles based on size does not distinguish between molecules and nanoparticles as many organic molecules contain more than $25$ atoms.
Nanoparticles can be more appropriately defined as an aggregate of atoms, with a radius between 1 nm and 100 nm, with dimensions less than the characteristic length of some physical phenomena.
When particle size is less than the characteristic length of some physical phenomena, the particles show different properties. The nanoparticles show unique properties that change with their size. Classical mechanics is able to explain the properties of bulk materials but is unable to explain the properties of nanoparticles. Quantum mechanical principles have to be used to explain the properties of the nanoparticles.
Properties of Nanoparticles
As discussed earlier, the properties of nanoparticles are different from the bulk material. The properties of nanoparticles also vary with size and shape. Hence different properties can be obtained by changing the size and shape of the nanoparticles. Some of the properties of nanoparticles are as follows :
1) Optical properties: The color of nanoparticles is different from the bulk material. When a bulk material is reduced in size to a few hundred atoms, the energy band structure of the bulk material changes to a set of discrete energy levels. Atomic clusters of different sizes will have different energy level separations. As clusters of different sizes have different energy level separations, the color of the clusters (which are due to transitions between the energy levels) will depend on their size. Hence the size of the cluster can be altered to change the colour of a material. For example, gold in bulk form appears yellow but gold nanoparticles appear bright red in color. The medieval glass makers produced tinted glass with a beautiful variety of colors by dissolving metal particles like gold, silver, cobalt, iron, etc. Due to these metal nanoparticles, the glasses appear colored.
In semiconductor nanoparticles (which are used in quantum dots) there is a significant shift in the optical absorption spectra towards blue as the particle size is reduced.
2) Electrical properties: The resistivity in bulk matter is mainly due to the scattering of electrons by ions and crystal defects. In nanostructures, the resistivity mainly depends on scattering from the boundaries of nanoparticles when particle size becomes less than the mean free path between collisions. Thus smaller particle size increases the resistivity.
Various types of defects in the lattice also increase the resistivity by limiting the mean free path. However many nanostructures are too small to have internal defects.
Another effect of reduced size is the confinement of conduction electrons. In bulk conductors, the electrons move freely throughout the entire conductor. The situation changes when one or more dimensions of the conductor are made very small.
Consider a flat conducting plate with a large length and width but a small thickness in the range of a few nanometers. In this configuration, called a quantum well, the electron will be confined along one dimension but will move freely along the remaining two dimensions.
If a conducting wire has a long length but a very small diameter, the electrons can move freely along the length but will be confined in two mutually perpendicular transverse directions. This configuration is known as a quantum wire.
If all three dimensions of the conductor are in nanometer range, the configuration is called a quantum dot and the electron is confined in all three dimensions. Confinement of electrons to small dimensions leads to quantization of energy.
The level of doping in semiconductors gives rise to another important phenomenon. For typical doping levels of 1 donor impurity atom in $10^{8}$ atoms of semiconductor atoms, a quantum dot of $10^{7}$ semiconductor atoms would have an average of $10^{-1}$ electrons. In other words, on an average, one quantum dot in 10 will have a free electron. These result in the phenomena of single-electron tunneling and coulomb blockade. The conduction is due to the tunneling of electrons through the quantum dot. The electrons are blocked from tunneling except at discrete voltage change positions. This phenomenon is called coulomb blockade. The I-V characteristic shown in the above Figure is called the coulomb staircase.
3) Magnetic properties: Magnetic properties are basically due to the orbital and spin motions of electrons around the nucleus. Every electron in an atom has spin and orbital magnetic moment which, when added, gives the total magnetic moment of the electron. The vector sum of all the moments of electrons gives the total moment of the atom. In most of the atoms, the net magnetic moment is zero.
However, atoms like iron, cobalt, and manganese, have a net magnetic moment. Crystals of these become atoms ferromagnetic when magnetic moments of all atoms are aligned in the same direction. The magnetic moment of magnetic nanoparticles is observed to be less than the value for perfect alignment of all moments. The net magnetic moment is observed to decrease with increasing temperature. This is due to thermal vibration of atoms in the cluster which disturbs the alignment of magnetic moments.
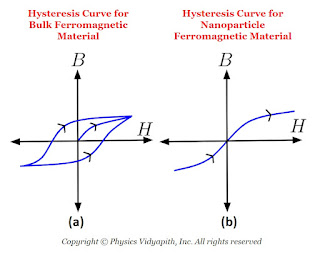
In bulk ferromagnetic materials, the magnetic moment is less than the moment the material would have if every atomic moment were aligned in the same direction. This is due to the presence of 'domains' which are regions in which all atomic moments are in one direction but moments of different domains are in different directions. When bulk ferromagnetic materials are subjected to alternating magnetic fields, they show hysteresis for which the B-H curve is shown in the above Figure (a). In nanosized ferromagnetic particles, essentially consisting of a single domain, there is no hysteresis and the $B-H$ curve is as shown in the above Figure (b). These particles are called the superparamagnetic.
The saturation magnetization is observed to increase significantly on decreasing the particle size. Another interesting property of nanoparticles is that clusters made of up nonmagnetic atoms like rhenium show magnetic moment which increases with the decrease in particle size.
4) Structural properties: The structure of small nanoparticles can be entirely different from that of the bulk material. The crystal structure of large nanoparticles is observed to be the same as the bulk material but with different lattice parameters. As a result of the changed structure, the electronic structure changes which in turn leads to changes in optical properties and reactivity. (TWD)
5) Mechanical properties: Mechanical properties like hardness, elasticity, and ductility depend upon the bonds between atoms. Imperfections in the crystal structure and impurities result in changes in these properties. As the nanoparticles are highly pure and free from imperfections, they show different mechanical properties than the bulk material. It has been observed that Young's modulus decreases in metallic nanocrystals with a decrease in particle size. The yield stress has been observed to increase with the decrease in grain size in bulk materials with nanosized grains. Hence stronger materials can be produced by making materials with nanosized grains. The carbon nanotubes are estimated to be about 20 times stronger than steel.
Showing posts with label Nanoscience & Nanotechnology. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Nanoscience & Nanotechnology. Show all posts
Preparation of nanostructured particles by sol-gel method
Introduction:
The advent of the sol-gel process occurred in the year $1921$. In the $1960s$, its development was given due to the need for new synthesis methods in the nuclear industry.
The sol-gel method is a widely used wet chemical technique to fabricate nanostructured materials. This technique is used to prepare nanoparticles of ceramics, glassy, and composite materials at relatively low temperatures based on wet chemical processing. It involves the conversion of a precursor solution (i.e. sol) into a solid three-dimension network (i.e. gel) through hydrolysis and condensation reactions of precursor compounds. There are following steps are given below to fabricate nanostructured material through the sol-gel method.
1. Precursor Compound Selection:
The first step involves selecting the appropriate precursor compounds, usually metal alkoxides or inorganic salts, that will form the desired material upon hydrolysis and condensation. These precursors should be soluble in a solvent i.e. metal salt in water or metal alkoxide in an organic solvent like alcohol.
2. Hydrolysis (Formation of Sol):
It involves the conversion of a homogeneous solution of the precursor into a colloidal solution (i.e. The colloidal particles of precursor stably disperse in a solvent is called a Sol or colloidal solution.). In the hydrolysis process, Alcohol like ethanol or isopropanol is used as a solvent. Water or an acidic/basic catalyst is then introduced to initiate hydrolysis of the precursor molecules. This results in the breaking of metal-oxygen bonds in the precursor, generating metal hydroxide or oxide species. The reactions are given below.
$M-OR + H_{2}O \rightarrow M-OH +R-OH$
Where
$M=OR \rightarrow$ Metal Alkoxide
$M-OH \rightarrow$ Metal Hydroxide
$M \rightarrow Si, Ti,\: Zn,\: Al,\: Sn \:\: etc $
3. Condensation (Formation of Gel):
The colloidal solution is kept for aging. During aging, the various condensation chemical reaction (i.e. polymerization) between two metal hydroxyl species leads to $M-O-M$ bonds with the release of $h_{2}O / R-OH$. This condensation process continues till finally results in a gel interconnected, rigid, and porous inorganic networks covered completely with the liquid phase. This transformation is known as a sol-gel transition.
4. Gelation:
As the condensation reactions continue, the sol transforms into a three-dimensional network with a continuous solid phase interspersed with a liquid phase. This semi-solid network is known as a gel. The gelation process can be controlled by adjusting factors like precursor concentration, solvent composition, pH, and temperature.
5. Drying:
Once the gel has formed, the excess solvent is removed through a drying process. The drying can be done by various techniques such as evaporation, supercritical drying, or freeze-drying. Careful drying is essential to prevent cracking or collapse of the gel structure.
6. Xerogel:
If the solvent is dehydrated under ambient conditions (i.e. Removal of $R-OH$ groups). Xerogel is produced.
7. Calcination:
In many cases, the dried gel must undergo a thermal treatment called calcination. This involves heating the gel at elevated temperatures to remove any remaining organic components and to induce further crystallization and growth of the desired material. The final crystalline structure and properties of the nanostructured material are developed during this step.
8. Characterization:
The resulting nanostructured material is then characterized using various techniques like X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and spectroscopy to analyze its composition, structure, particle size, and morphology.
Advantages of the Sol-gel process:
Versatile: Sol-gel method provides better control over the structure of particles, size of particles, and porosity. There is a possibility of incorporating nanoparticles and organic materials into sol-gel derived oxides.
Extended composition ranges: The sol-gel method allows the preparation of any oxide composition as well as also some non-oxides and the production of new hybrid organic-inorganic materials, which do not exist naturally.
Better Homogeneity: Due to mixing at the molecular level; high purity
Less energy consumption: There is no requirement for the melting temperature since the three-dimensional network structure can be achieved at relatively low temperatures.
Coating and thin films, monoliths, composites, porous membranes, powders, and fibers.
No need for special or expensive equipment.
Disadvantages of Sol-Gel:
Cost of precursors
Shrinkage of a wet gel upon drying, which often leads to fracture due to the generation of large capillary stresses and consequently, makes difficult the attainment of large monolithic pieces
Preferential precipitation of a particular oxide during the formation of colloidal solution i.e. Sol (in multicomponent glasses) due to the different reactivity of the alkoxide precursors
Difficult to avoid residual porosity and $OH$ groups.
Application of Sol-Gel:
Protective Coating
Thin films and fibers
Opto-mechanicalspan
Nanoscale powders
Medicine
$M-OH \rightarrow$ Metal Hydroxide
$M \rightarrow Si, Ti,\: Zn,\: Al,\: Sn \:\: etc $
$M-OR + HO=M \rightarrow M-O-M +R-OH$
Synthesis of Nanomaterials
In the field of nanomaterials, there are two main approaches to their synthesis and fabrication.
A.) Top-Down Approach
B.) Bottom-up Approach
These two approaches are based on the methods used to create or assemble nanoscale materials and structures.
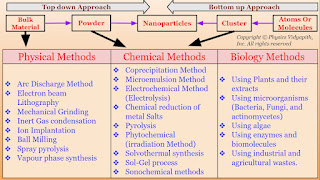
A.) Top-Down Approach: In this approach, large-scale materials (i.e. Bulk materials) are broken down into smaller and smaller components until they reach the desired nanoscale dimensions i.e. firstly the bulk material is converted into powder form and then the powder's form is converted into nanoparticles. There are various physical methods (like Arc discharge method, Electron beam lithography, Mechanical grinding, etc) used to convert the bulk material into powder form and powder form is converted into nanoparticles by chemical methods (like Sol-Gel Process, Electrochemical method, Microemulsion etc.).
One of the challenges with the top-down approach is that it may lead to a lack of control over the final nanomaterial's properties and may also generate waste during the process.
Top-down approaches are based on grinding the material. Thus these processes are subtractive in nature. The parts of mechanical devices used to shape the objects are stiff and hard, so these approaches are not suitable for soft samples. The top-down approach assumes that nanodevices must be produced piece by piece in a series of steps, much like manufactured goods are made. Scanning probe microscopy (SPM) is an important technique used both for the synthesis and characterization of nanomaterial by a top-down approach. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) tips can be used as a nanoscale "write head" to deposit a resist, which is then followed by an etching process to remove material in a top-down approach.
Some common techniques used in the top-down approach include:
a.) Mechanical milling: High-energy mechanical forces are applied to break down large particles into smaller ones, eventually reaching the nanoscale range.
b.) Lithography: Techniques like electron beam lithography or photolithography are used to create patterns on a substrate, defining the nanoscale features.
c.) Etching: Chemical or plasma etching is used to remove material from a larger sample, creating nanoscale structures.
d.) Nanolithography: Specialized lithography techniques are used to directly write or print nanoscale patterns on material.
Advantages of the Top-down Approaches:
1.) This Top-down approach is often suitable for large-scale production of nanomaterials, making it economically viable.
2.) Many top-down approaches have been widely used and optimized for bulk materials, which can be adapted for nanomaterial synthesis.
3.) This approach allows precise control over the size and shape of the resulting nanomaterials.
4.) Suitable for laboratory experimentation.
Disadvantages Top-down Approaches:
1.) It is required large installations and huge capital is required for building their setup.
2.) These approaches are quite expensive.
3.) The growth process is slow and hence these approaches are not suitable for large-scale production.
4.) The biggest problem in the approach is the imperfection of surface structure.
5.) The mechanical and chemical processes involved in the top-down approach can introduce defects in the nanomaterials, affecting their properties.
6.) This approach generates a significant amount of waste during the material reduction process, which can be environmentally problematic.
7.) As the approach starts with larger structures and reduces their size, it may be challenging to achieve precise control over nanoscale features, leading to variations in properties.
B.) Bottom-up Approaches: In this approach, It involves atom-by-atom, molecule-by-molecule, or cluster-by-cluster manipulation for the synthesis of nanostructures. It means that atoms are assembled into molecules, molecules are assembled into clusters, and the clusters are assembled to form the nanoparticle. This approach relies on self-assembly and controlled growth to create the desired nanoscale structure.
The bottom-up approach is based on the principle of molecular recognition (that is self-assembly). Self-assembly means growing more and more things of one's kind from themselves. The principle of self-assembly (shake and bake) involves assembling precursors in random positions and orientations, providing energy (shaking) to enable them to explore configuration space. The hugeness of this space suggests that a convergent pathway is inherent in the process in order to allow it to be completed in a reasonable time. Once the precursors are in position, "baking" may be required to strengthen the bonds connecting them and fix the final object permanently.
Some common techniques used in the bottom-up approach include:
a.) Chemical Synthesis: Chemical reactions are used to build up nanomaterials from atomic or molecular precursors, allowing precise control over the final product's size and shape.
b.) Self-Assembly: Molecules or nanoparticles are designed to interact in a way that leads to their spontaneous arrangement into specific nanoscale structures.
c.) Vapor Deposition: Nanoscale materials are grown layer by layer on a substrate by allowing precursor gases to react on its surface.
d.) Sol-Gel Process: Nanomaterials are formed by hydrolyzing metal alkoxides in a solution, followed by gelation and controlled drying.
The bottom-up approach allows for greater control over the nanomaterial's properties and can potentially lead to unique properties not found in their bulk counterparts. However, it can be more challenging to scale up these processes for mass production compared to the top-down approach.
Advantages of Bottom-down Approaches:
1.) The bottom-up approach allows for precise control at the atomic or molecular level, leading to well-defined nanomaterials with specific properties.
2.) Since the materials are assembled from individual atoms or molecules, there are fewer defects compared to the top-down approach.
3.) Bottom-up synthesis can result in unique nanomaterials with properties not easily achievable through top-down approaches.
Disadvantages of Bottom-down Approaches:
1.) Bottom-up approaches can be more complex and expensive, especially for large-scale production.
2.) Some bottom-up approaches may not be easily scalable for mass production, limiting their industrial applicability.
3.) Achieving high purity and reproducibility in bottom-up synthesis can be challenging due to the intricate processes involved.
Both the top-down and bottom-up approaches have their advantages and disadvantages, and researchers often choose the most suitable method based on the specific properties and applications of the nanomaterial they aim to create. Additionally, a combination of these approaches, known as "hybrid approaches," can be used to achieve even more complex nanoscale structures with tailored properties.
The synthesis of nanomaterial according to technique:
1.) Physical Methods
2.) Chemical Methods
3.) Biological Methods
1.) Physical Methods: Nanoparticles may be synthesized using a number of physical methods which are listed below. These methods are of two types viz mechanical type and vapor deposition type. These methods work at very high temperatures. The highest working temperatures are usually greater than $350^{\circ}C$.
- Arc Discharge Method
- Electron beam Lithography
- Mechanical Grinding
- Inert Gas condensation
- Ion Implantation
- Ball Milling
- Spray pyrolysis
- Vapour phase synthesis
- Coprecipitation Method
- Microemulsion Method
- Electrochemical Method (Electrolysis)
- Chemical reduction of metal Salts Pyrolysis
- Phytochemical (irradiation Method)
- Solvothermal synthesis
- Sol-Gel process
- Sonochemical methods
- Using Plants and their extracts
- Using microorganisms (Bacteria, Fungi, and actinomycetes)
- Using algae
- Using enzymes and biomolecules
- Using industrial and agricultural wastes
Basics and types of Nanomaterials
What is a nanoparticle?
Those particles that have size ranges between $1$ to $100 \: nanometres$ are called a nanoparticle. The particles are undetectable by the human eye. There are significant differences in the properties (like magnetic, electrical, Structural, Mechanical, and optical properties) of nanoparticles and bulk materials.
What is nanomaterial?
Those materials that have at least one dimension should be in nanometres i.e. $10^{-9}m$ are called nanomaterials. The prefix 'nano' means a billionth $(10^{-9})$.
Types of nanomaterials
There are two types of nanomaterial that can be classified:
A.) On the basis of dimension
B.) On the basis of material
A.) On the basis of dimensions: According to Siegel, nanostructured materials are classified on the basis of dimension:
1.) Three-dimensional nanomaterials (Bulk Nanomaterial)
2.) Two-dimensional nanomaterials (Quantum Well)
3.) One-dimensional nanomaterials (Quantum Wire)
4.) Zero-dimensional nanomaterials (Quantum Dot)
1.) Three-dimensional nanomaterials (Bulk Nanomaterial): These nanomaterials have not confined to the nanoscale range in any dimension. These materials have three arbitrary dimensions above the nanoscale i.e. $100 nm$. The bulk three-dimensional nanomaterials are composed of a multiple arrangement of nano-size crystals in different orientations. The three-dimensional nanomaterials or bulk nanomaterials can be used as bundles of nanowires, dispersion of nanoparticles, and nanotubes as well as multi-nano layers (polycrystals) in which the $0D$, $1D$, and $2D$ structural elements are in very close contact with each other and form interfaces.
2.) Two-dimensional nanomaterials (Quantum Well): These nanomaterials have one dimension in the nanoscale. It is also called a quantum well. This means that the particles of material are confined only along one dimension. The 2D nanomaterials exhibit plate-like shapes. It includes nanofilms, nanolayers, and nanocoatings with nanometre thickness.
3.) One-dimensional nanomaterials (Quantum Wire): These nanomaterials have two dimensions in the nanoscale. It is also called quantum wire. This means that the particles of material are confined in two dimensions. This leads to needle-shaped nanomaterials. It includes nanofibers, nanotubes, Nanorods, and nanowires.
4.) Zero-dimensional nanomaterials (Quantum Dot): These nanomaterials have all three dimensions in the nanoscale i.e., no dimensions are greater than $100 nm$. It is also called quantum dots. This means that the particles of material are confined in all three dimensions. It includes Nanospheres and nanoclusters.
B.) On the basis of materials: Nanomaterials can be categorized on the basis of material into four types such as:
1.) Inorganic-based nanomaterials (Metal-based materials ):
2.) Carbon-based nanomaterials:
3.) Organic-based nanomaterials (Dendrimers):
4.) Composite-based nanomaterials.
1.) Inorganic-based nanomaterials (Metal-based materials ):
Generally, inorganic-based nanomaterials include different metal and metal oxide nanomaterials.
Examples of metal-based inorganic nanomaterials - silver $(Ag)$, gold $(Au)$, aluminum $(Al)$, cadmium $(Cd)$, copper $(Cu)$, iron $(Fe)$, zinc $(Zn)$, and lead $(Pb)$ nanomaterials.
Examples of metal oxide-based inorganic nanomaterials- zinc oxide $(ZnO)$, copper oxide $(CuO)$, magnesium aluminum oxide $(MgAl_{2}O_{4})$, titanium dioxide $(TiO_{2})$, cerium oxide $(CeO_{2})$, iron oxide $(Fe_{2}O_{3})$, silica $(SiO_{2})$, and iron oxide $(Fe_{3}O_{4})$, etc.
(2) Carbon-based nanomaterials:
Carbon-based nanomaterials are graphene, fullerene, single-walled carbon nanotube, multi-walled carbon nanotube, carbon fiber, activated carbon, and carbon black.
(3) Organic-based nanomaterials (Dendrimers):
The organic-based nanomaterials or dendrimers (i.e. Dendrimers are repetitively branched molecules. Dendrimers name comes from the Greek word ‘dendron’ which means tree.) are formed from organic materials that do not include carbon materials, for instance, dendrimers, cyclodextrin, liposome, and micelle.
(4) Composite-based nanomaterials: The composite nanomaterials can be any combination of all nanomaterials like metal-based, carbon-based, metal oxide-based, and organic-based nanomaterials. These composite nanomaterials have very complicated structures like a metal-organic framework.
Popular Posts
-
Let $S$ be a point monochromatic source of light of wavelength $\lambda$ placed at the focus of collimating lens $L_{1}$. The light beam is ...
-
Angle of Acceptance → "If incident angle of light on the core for which the incident angle on the core-cladding interface equals t...
-
Derivation of interference of light due to a wedge-shaped thin film: Interference of light due to wedge-shaped thin film The wedge...
-
Maxwell's Equations: Maxwell's equation of the electromagnetic wave is a collection of four equations i.e. Gauss's law of elec...
-
Let a plane wavefront be incident normally on slit $S_{1}$ and $S_{2}$ of equal $e$ and separated by an opaque distance $d$.The diffracted l...
Study-Material
Categories
Alternating Current Circuits
(10)
Atomic and Molecular Physics
(4)
Biomedical
(1)
Capacitors
(6)
Classical Mechanics
(12)
Current carrying loop in magnetic field
(5)
Current Electricity
(10)
Dielectric Materials
(1)
Electromagnetic Induction
(3)
Electromagnetic Wave Theory
(23)
Electrostatic
(22)
Energy Science and Engineering
(2)
Error and Measurement
(2)
Gravitation
(11)
Heat and Thermodynamics
(3)
Kinematics Theory Of Gases
(2)
Laser System & Application
(15)
Magnetic Effect of Current
(9)
Magnetic Substances
(3)
Mechanical Properties of Fluids
(5)
Nanoscience & Nanotechnology
(4)
Nuclear Physics
(7)
Numerical Problems and Solutions
(2)
Optical Fibre
(5)
Optics
(25)
Photoelectric Effect
(3)
Quantum Mechanics
(37)
Relativity
(8)
Semiconductors
(2)
Superconductors
(1)
Topic wise MCQ
(9)
Units and Dimensions
(1)
Waves
(5)



.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




