Superconductivity
The property of a substance in which the electrical resistance of the substance is zero at very low temperatures. This property of substance is called superconductivity.
For certain substances, like mercury, the resistivity suddenly drops to zero at very low temperatures typically near the boiling point of liquid helium. Some metals, doped semiconductors, alloys and ceramics (i.e. these are insulators at room temperature and superconduct at higher temperatures than the metals) show superconductivity.
Temperature Dependence of Resistivity
In superconducting substances, the resistivity suddenly drops to zero at a particular temperature known as critical temperature ($T_{c}$) or
transition temperature and remains zero below that as shown in Figure below.
The critical temperature for mercury is $4.2 K$. Below this critical temperature, mercury is superconducting whereas above this temperature it behaves like a normal conductor. Different superconducting materials have different critical temperatures but the nature of the variation in resistivity with temperature remains more or less similar.
Properties of Superconductors
1.) Zero electrical resistance:
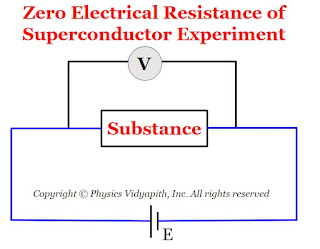
The electrical resistivity of superconductors is zero at very low temperatures. The experimental testing of zero resistance was tried by
connecting the substance at room temperature to a battery. A voltmeter was connected across the specimen to measure the electric potential difference across the specimen as shown in Figure below.
As the temperature of the substance gets lowered. It was observed that below a particular temperature (i.e. critical temperature), the electric potential difference across the substance suddenly dropped to zero.
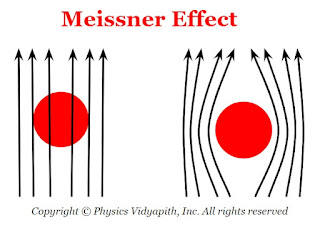
2) Meissner effect:
When a substance is placed in a weak magnetic field and cooled below the critical temperature then this substance behaves like perfect diamagnets with zero magnetic induction. This phenomenon is called the Meissner effect.
The magnetic induction inside the substance in the normal state is given by, Superconductors
$B = \mu_{\circ} (H +M)$
where $H$ is the externally applied magnetic field and $M$ is the magnetization inside the substance.
When the temperature $T$ of the specimen is lowered below its critical temperature
$B= 0$
$M_{\circ}(H + M) = 0$
$H = - M$
The susceptibility $\chi$ is given by,
$\chi=\frac{M}{H}$
For diamagnetic substance $\chi=-1$
As the relative permeability
$\mu_{r}=1+\chi$
$\therefore \mu_{r}=0$
This indicates perfect diamagnetism.
Meissner effect cannot be explained by assuming that the superconductor is a perfect conductor with zero electrical conductivity. The electric field is given by,
$E=\frac{V}{l}$
$E=\frac{iR}{l}$
$E=\frac{iR}{l} \frac{A}{A}$
$E=\frac{RA}{l} \frac{i}{A}$
$E=\rho J$
Where
$\rho$ = Resistivity
$J$= Current density
If $\rho$ becomes zero for a finite current density $J$, then $E =0$.
From Maxwell's equations,
$\nabla \times \overrightarrow{E} = \frac{d \overrightarrow{B}}{dt}$
As $E=0$, $\frac{d \overrightarrow{B}}{dt} =0$
$\therefore \overrightarrow{B} = Constant$
$\therefore$ In a conductor the flux cannot change on cooling below the critical temperature. This contradicts the Meissner effects according to which the flux must reduce to zero and hence superconductor is not just a perfect conductor.
Due to the Meissner effect, superconductors strongly repel external magnets which leads to magnetic levitation.
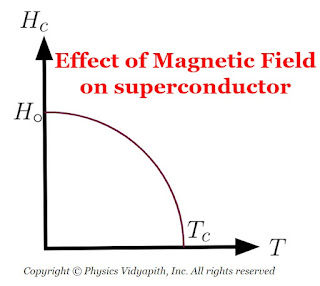
3) Effect of magnetic field on superconductors :
Superconductivity is destroyed by sufficiently strong magnetic fields. The minimum value of the applied magnetic field required to destroy
superconductivity is called the critical field $H_{c}$. and is a function of temperature. Above the critical temperature $T_{c}$, $H_{c} = 0$. Below the critical temperature, the variation of $H_{c}$, with temperature $T$ is as shown in Figure below and be represented by the equation
$H_{c}=H_{\circ} \left[ 1- \left(\frac{T}{T_{c}}\right) \right]$
where $H_{\circ}$ is the critical field at absolute zero.
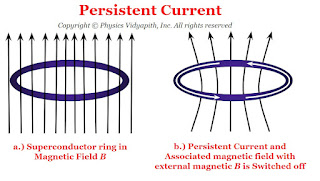
4) Persistent currents :
When a ring is placed in the magnetic field and the field is switched off, a current is induced in the ring. This induced current is called the persistent current.
The magnitude of current remains constant even though there is no source of e.m.f. as the resistance of the superconducting ring is zero. These currents flowing in the ring produce magnetic fields that do not require any power supply to maintain a constant field.
5) Isotope effect :
According to observations, the critical temperature of superconductors varies with isotopic mass. The critical temperature is smaller for larger isotopic mass. This phenomenon is called the isotope effect.
The relation between critical temperature $T_{c}$ and isotopic mass $M$ is given by,
$T_{c}M^{a} = Constant$
For most of the materials $a =\frac{1}{2}$
$\therefore T_{c}M^{\frac{1}{2}} = Constant$
$\therefore T_{c} \propto M^{-\frac{1}{2}} $
As lattice vibrations are reduced for larger isotopic masses, the isotope effect indicates that superconductivity is due to the interaction between electrons and lattice vibrations.
6) Critical Current:
All the current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. Similarly, When current flows through a superconducting wire, a magnetic field is produced around it. If the current in the superconducting wire is increased, the magnetic field intensity just outside it will increase and reach the critical field $H_{c}$. If the current is increased beyond this value, the wire will be subjected to a magnetic field exceeding the critical field due to which the superconducting state will be destroyed and then it will revert to its normal state. The maximum current that a superconductor can carry without reverting back to its normal state is known as critical current.
The magnetic induction due to a wire of radius $r$ just outside it is
$B=\frac{\mu_{\circ}i}{2 \pi r}$
$\mu_{\circ} H=\frac{\mu_{\circ}i}{2 \pi r}$
$H=\frac{i}{2 \pi r}$
If the critical current in $_{c}$, and critical field is $H_{c}$, ,
$H_{c}=\frac{i_{c}}{2 \pi r}$
$i_{c}=2 \pi r H_{c}$
Types of Superconductors
There are two types of superconductors based on the difference in magnetization exhibited by them. These are known as Type-I (or soft) and Type-II (or hard) superconductors.
1) Type-I Superconductors (Soft superconductors):
The magnetization curve for a Type-I -M superconductor is shown in Figure below. Type-I superconductors show the complete Meissner effect when the applied magnetic field H is less than the critical field $H_{c}$.
The magnetization in the superconductor is proportional to the applied field and the superconductors behave like perfect diamagnet.
For $H > H_{ç}$, the magnetization is negligible and the superconductor becomes a normal conductor. Pure elements show such magnetization curves. The values of $H_{c}$, are very low.
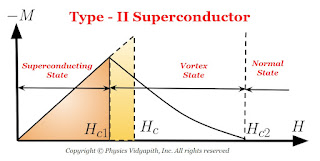
2) Type-II Superconductors (Hard superconductors)
The magnetization curve for a type-II superconductor is shown in Figure below.
There are two critical field $H_{c1}$ and $H_{c2}$ in Type-II superconductors that characterize it. Upto the lower critical field $H_{c1}$, the superconductor is perfectly diamagnetic and flux is completely ejected out from the superconductor. The magnetization in the superconductor is proportional to the applied field. Between $H_{c1}$ and $H_{c2}$, the Meissner effect is incomplete but electrically it is a superconductor but not magnetically. This state is called the mixed state or the vortex state.
The values of $H_{c}$ may be $100$ times or higher than the critical field $H_{c}$, for type-I superconductors.
Above the higher critical field $H_{c2}$ the superconductor becomes a normal conductor.
Type-II superconductors are usually alloys or transition metals with high values of electrical resistivity in the normal state.
High-Temperature Superconductors
Kamerlingh Onnes discovered superconductivity in mercury in 1911 with a critical temperature of $4.2 K$. The research was then focussed on materials with larger critical temperatures so that the phenomenon could become commercially viable.
But, till about 1986, the highest critical temperatures were observed to be nearly $20 K$. In 1986, an oxide of lanthanum, barium, and copper ($La_{1.85} Ba_{0.15} CuO_{4}$) was observed to have a critical temperature of $36 K$. In 1987, an oxide of yttrium, barium and copper ($YBa_{2}Cu_{3},0_{7}$) was found to have a critical temperature of $90 K$ and then an oxide of thallium, barium, calcium and copper($Tl_{2}Ba_{2}Ca_{2}Cu_{3}O_{10}$) was found to have a critical temperature of $120 K$.
The presence of parallel sheets of $CuO_{2}$ is the main feature of high-temperature superconductors.. Efforts are going on to find superconductors with critical temperatures near room temperature.
$J$= Current density