Motion of body in a vertical circle and its Practical Applications
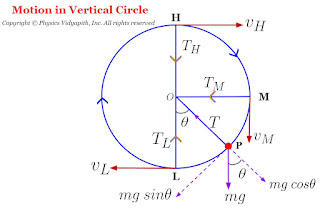
Calculation of Motion of a body in a vertical Circle: Let us consider, A body that has mass $m$ moving in a vertical circle of radius $r$. If at any instant the body is at position $P$ with angular displacement $\theta$ from the lower position $L$ of the circle. As shown in the figure below.
The various forces acting on the body are:
The weight $mg$ of the body, acting vertically downwards
Tension $T$in the string acting along the $PO$. Now $mg$ can be resolved into two components:
1.) The horizontal component $mg cos\theta$ opposite to $T$
2.) The vertical component $mg sin\theta$ act along tangent to the circle at $P$
So the net force on the body at position $P$ provides the necessary centripetal force required by the body
$T-mg cos\theta = \frac{m v^{2}}{r}$
$T= \frac{m v^{2}}{r} + mg \: cos\theta \qquad(1)$
Tension and velocity at the highest position $H$ of the verticle circle: At the highest position $H$ the tension $T_{H}$ of the will be minimum and the velocity $v_{H}$ will also be minimum.
If $cos\theta = -1$ i.e. $\theta=180^{\circ}$
Then Tension $T$ and velocity $v$ will be minimum i.e $T_{H}$ and $v_{H}$
so from equation $(1)$
$T_{H}= \frac{m v_{H}^{2}}{r} - mg $
So from the above equation, we can conclude that The body will move along the vertical circle only when $T_{H} \geq 0$
$\left( \frac{m v_{H}^{2}}{r} - mg \right) \geq 0$
$ \frac{m v_{H}^{2}}{r} \geq mg $
$ \frac{ v_{H}^{2}}{r} \geq g $
$ v_{H} \geq \sqrt {rg} $
Thus the minimum value of the velocity at the highest position is $\sqrt{rg}$
Tension and velocity at lowest position $L$ of the verticle circle: At the lowest position $L$ the tension and velocity will be maximum. Now applying the principle of energy conservation for the position $H$ and $L$ of the body.
Total energy at $L$ =Total energy at $H$
$\frac{1}{2}m v_{L}^{2}=\frac{1}{2}m v_{H}^{2} +mg(2r)$
Now substitute the value of $v_{H} \geq \sqrt{gr}$ in above equation then we get
$\frac{1}{2}m v_{L}^{2}=\frac{1}{2}m (gr) +mg(2r)$
$\frac{1}{2}m v_{L}^{2}=\frac{5mgr}{2}$
$v_{L} \geq \sqrt{5gr}$
For the maximum value of tension $T_{L}$ at the lowest position $L$ of the vertical circle. Now put $cos \theta =1$ i.e $\theta=0^{\circ}$ in the equation $(1)$ then we get
$T_{L}= \frac{m v_{L}^{2}}{r} + mg $
Now substitute the value of $v_{L} \geq \sqrt{5gr}$ in the above equation then
$T_{L} \geq \frac{m 5gr}{r} + mg $
$T_{L} \geq 6gr$
Tension and velocity at horizontal position $M$ of the verticle circle:
Now apply the principle of conservation of energy for position $M$ and position $L$
Total energy at $M$ =Total energy at $L$
$ \frac{1}{2}m v_{M}^{2} + mgr = \frac{1}{2} m v_{L}^{2}$
$ \frac{1}{2}m v_{M}^{2} = \frac{1}{2} m v_{L}^{2} - mgr$
Now substitute the value of $v_{L} \geq \sqrt{5gr}$ in the above equation then
$ \frac{1}{2}m v_{M}^{2} \geq \frac{1}{2} m 5gr - mgr$
$ \frac{1}{2}m v_{M}^{2} \geq \frac{3 mgr}{2}$
$v_{M}^{2} \geq 3 gr$
$v_{M} \geq \sqrt{3 gr}$
To find the tension $T_{M}$ at position $M$ substitute the $cos \theta =0$ i.e $\theta =90^{\circ}$ in equation $(1)$. Then we get
$T_{M} = \frac{m v_{M}^{2}}{r} + 0$
$T_{M} = \frac{m v_{M}^{2}}{r}$
Now substitute the value of $v_{M} \geq \sqrt{3gr}$ in the above equation. Then we get
$T_{M} \geq 3mg$
Practical Application of motion in a vertical Circle:
1.) When a bucket containing water is rotated in a vertical circle with a velocity at the lowest point $v_{L} \geq \sqrt{5gr}$, water shall not spill even at the highest point, when the bucket is upside down. If the bucket is whirled slowly, so that $ \left(mg \gt \frac{mv_{H}^{2}}{r} \right) $, then a part of the weight shall provide the necessary centripetal force $\left( \frac{mv_{H}^{2}}{r} \right)$; and the rest of the weight of water $\left( mg - \frac{mv_{H}^{2}}{r} \right) $ causes some water to accelerate downwards and spill. Only this much water shall leave the bucket.
2.) A pilot of an aircraft can successfully loop a vertical loop without falling at the top of the loop (being without a belt) when its velocity at the bottom of the loop is $\geq \sqrt{5gr}$
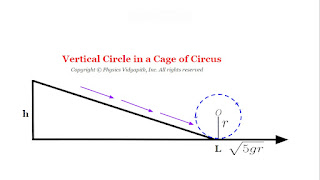
3.) In a circus, a motorcyclist is able to perform the feat of driving the motorcycle along a vertical circle in a cage. The motorcyclist does not fall even at the highest point, when his velocity at the bottom of the cage is $\geq \sqrt{5gr}$.
To acquire this velocity at the lowest point $L$ of the vertical circle of radius $r$, he has to roll down a vertical height $h$, As shown in the figure below:
From the equation of motion $v^{2}=u^{2}+2as$
Let $u=0$, $a=+g$ and $s=h$
we get, $v^{2}=0 +2gh$
$v=\sqrt{2gh}$
To move in a vertical circle, the velocity $v$ acquired at $L$ must at least be equal to $\sqrt{5gr}$. i.e.
$\sqrt{2gh}= \sqrt{5gr}$
$h=\frac{5r}{2}$