What is an electric charge?
Electric charge is an intrinsic property of elementary particles (e.g., electrons, protons, neutrons, etc.) of any substance that gives rise to electric force between them when they get closer.
Types of charge:
There are two types of electric charge
1.) Positive Electric Charge like Proton
2.) Negative Electric Charge like Electron
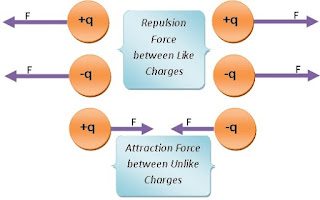
The same nature of charged particles repels each other and the opposite nature of charged particles attracts each other. For example, electrons and electrons repel each other, and electrons and protons attract each other. Similarly, proton and proton repel each other.
Generally, any substance is electrically neutral because the number of electrons and protons are equal in it but according to the
Free electron Model theory, these substances are classified into three categories. These are:
1.) Conductor
2.) Semiconductor
3.) Insulator
The electric force is generated in conductors and insulating substances but not in semiconductor substances because these semiconductor substances have four electrons in their valence shells.
Generation of Electric force in Conductor:
The electric force is generated in conductors due to the transfer of electrons from one conducting substance to another conducting substance.
There are various methods for the transfer of electrons in conductors, like contact, friction, and induction. Therefore, When electrons are transferred from one conductor to another conductor then the conductor has deficiency or excess of electrons, these conductors are called electrostatically charged.
Electrostatic charged Conductors: The charge on the conductors due to the transfer of electrons between the conductors is known as electrostatic charged conductor.
There are two types of electrostatic-charged conductors.
1.) Positive Electrostatic Charged Conductor:
When conductors have a deficiency of electrons i.e. the number of electrons is less than protons, these conductors are called positive electrostatic charged conductors.
2.) Negative Electrostatic Charged Conductor:
When conductors have excessive electrons i.e. number of electrons is greater than protons, these conductors are called negative electrostatic charged conductors.
Generation of Electric force in Insulator:
Insulators are charged by induction this charging occurs due to the polarization of atoms of insulating substances. In the absence of an external electric field, the center of mass of the nucleus and electron cloud in an atom lies on the same point but when an insulating substance is placed in an external electric field, the center of mass of the nucleus and electron cloud in an atom is separated from each other at a very small distance. The center of mass of the electron cloud is shifted toward the positive side of the external electric field and the center of mass of the nucleus is shifted toward the negative side of the external electric field. thus these atoms are polarized. When insulators are electrically charged, these polarized atoms store the electric potential energy.
Basic Properties of Electric Charge:
1.) Additive Nature of Charge:
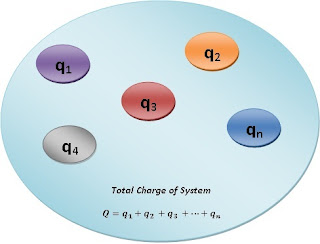
The total charge on any system is always equal to the algebraic sum of all the charges in the system.
If a system contains $'n'$ number of point charges, the total charge of a system will be the sum of $'n'$ number of point charges.
Let us consider, a system containing $'n'$ number of point charges like $q_{1},q_{2},q_{3}......q_{n}$, the total charge of the system will be
$Q=q_{1}+q_{2}+q_{3},.....+q_{n}$
$Q=\sum_{i}^{n}q_{i}$
2.) Conservation of Charge:
The total Charge of the isolated system is always conserved i.e.
The electric charges neither can be created nor destroyed i.e. The electric charges are generated due to transfer of electrons from one subtance to another substance.
3.) Quantization of Charge:
The electric charge is always an integer multiple of $‘e’$. It is known as the quantization of charge.
$Q=\pm ne$
Where $'n'$ is an integer number.
4.) The mass of charged particle depends on velocity:
The velocity of the charged particle is significant to the speed of light so the mass of the charged particle depends on the velocity. This variation can be found by following the formula:
$m=\frac{m_{0}}{\sqrt{1-\frac{v^{2}}{c^{2}}}}$
Where
$m_{0}$ - Rest mass of particle
$m$ - Relative mass of the particle