Electric field intensity at different points in the field due to uniformly charged thick hollow non-conducting sphere:
Let us consider, A hollow non-conducting sphere of inner radius $r_{1}$ and outer radius $r_{2}$ in which $+q$ charge is evenly distributed evenly in the entire volume of the sphere. If $\rho$ is the volume charge density then electric field intensity at different points on the electric field of the thick hollow non-conducting sphere:
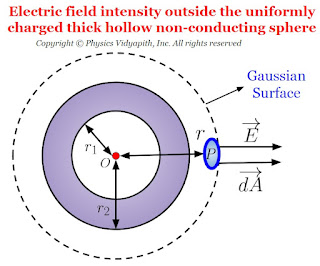
- Electric field intensity outside the thick hollow non-conducting sphere
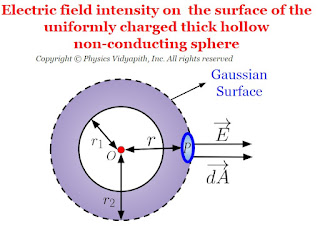
- Electric field intensity on the surface of the thick hollow non-conducting sphere
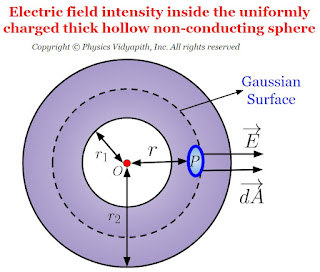
- Electric field intensity at an internal point of the non-thick hollow conducting sphere
1. Electric field intensity outside the thick hollow non-conducting sphere:
Let us consider, A point $P$ is outside the sphere which is at a $r$ distance from the center point $O$ of the sphere. The direction of electric flux is radially outward in the sphere. So the direction of the electric field vector and the small area vector will be in the same direction i.e. ($\theta =0^{\circ}$). Here $\overrightarrow {dA}$ is a small area element so the small amount of electric flux will pass through this area i.e. →
$ d\phi_{E}= \overrightarrow {E}\cdot \overrightarrow{dA}$
$ d\phi_{E}= E\:dA\: cos\: 0^{\circ} \quad \left \{\because \theta=0^{\circ} \right \}$
$ d\phi_{E}= E\:dA \qquad (1) \quad \left \{\because cos\:0^{\circ}=1 \right \}$
The electric flux passes through the entire Gaussian surface, So integrate the equation $(1)$
$ \oint d\phi_{E}= \oint E\:dA $
$ \phi_{E}=\oint E\:dA\qquad (2)$
According to Gauss's law:
$ \phi_{E}=\frac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}\qquad (3)$
From equation $(2)$ and equation $(3)$, we can write as
$ \frac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}=\oint E\:dA$
$ \frac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}= E\oint dA$
For entire Gaussian spherical surface is
$\oint {dA}=4\pi r^{2}$.
So from the above equations
$ \frac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}= E(4\pi r^{2})$
$ E=\frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_{0}}\frac{q}{r^{2}} \qquad(4)$
From the above equation, we can conclude that the behavior of the electric field at the external point due to the uniformly charged thick hollow non-conducting sphere is the same as the point charge i.e. like the entire charge is placed at the center.
Since the sphere is a non-conductor so the charge is distributed in the entire volume of the sphere. So charge on the thick hollow sphere-
$q=\frac{4}{3} \pi \left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right) \rho $
Substitute this value of charge $q$ in the above equation $(4)$, Therefore,
$ E=\frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_{0}}\frac{4\pi \left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)\: \rho}{3r^{2}}$
$ E=\frac{\rho}{3 \epsilon_{0}}\frac{\left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}{r^{2}}$
This equation describes the electric field intensity at the external point of the thick hollow non-conducting sphere.
2. Electric field intensity on the surface of the thick hollow non-conducting sphere:
If point $P$ is placed on the surface of the thick hollow non-conducting sphere i.e. ($r=r_{2}$). so electric field intensity on the surface of the thick hollow non-conducting sphere:
$ E=\frac{\rho}{3\epsilon_{0}}\frac{\left(r^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}{r^{2}}$
3. Electric field intensity at an internal point of the thick hollow non-conducting sphere:
If point $P$ is placed inside the sphere at the distance $r$ from the origin $O$, the electric flux which is passing through the Gaussian surface
$ \phi_{E}= E.4\pi r^{2}$
Where $\phi_{E}=\frac{q'}{\epsilon_{0}}$
$ \frac{q'}{\epsilon_{0}}=E.4\pi r^{2}$
Where $q'$ is part of charge $q$ which is enclosed with Gaussian Surface
$ E=\frac{1}{4 \pi \epsilon_{0}} \frac{q'}{r^{2}} \qquad \qquad (5)$
The charge is distributed uniformly in the entire volume of the sphere so volume charge density $\rho$ will be the same as the entire
sphere i.e.
$ \rho=\frac{q}{\frac{4}{3}\pi \left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}=\frac{q'}{\frac{4}{3}\pi \left(r^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}$
$ \frac{q}{\left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}=\frac{q'}{\left(r^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}$
$ q'=q\frac{\left(r^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right) }{\left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}$
Put the value of $q'$ in equation $(5)$, so
$ E=\frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_{0}}\frac{q} {r^{2}} \frac{\left(r^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right) }{\left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}$
Where $q=\frac{4}{3} \pi \left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right) \rho $. So above equation can be written as:
$ E=\frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_{0}}\frac{\frac{4}{3} \pi \left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right) \rho } {r^{2}} \frac{\left(r^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right) }{\left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}$
$ E=\frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_{0}}\frac{\frac{4}{3} \pi \left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right) \rho } {r^{2}} \frac{\left(r^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right) }{\left(r_{2}^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}$
$E=\frac{ \rho }{3 \epsilon_{0}} \frac{\left(r^{3}-r_{1}^{3} \right)}{r^{2}}$