Variation in Gravitational Acceleration:
The value of $g$ varies above and below the surface of the earth. It also changes with the latitude at different places and due to the rotation of the earth about its axis. The earth is not a perfect sphere but is approximately an ellipsoid. The radius of the earth is more at the equator and lesser at the poles. The acceleration due to gravity also changes due to the shape of the earth.
1.) Effect of Altitude on Acceleration due to Gravity
2.) Effect of depth below the earth's surface on Acceleration due to Gravity
3.) Effect of the shape of the earth
4.) Effect of rotation about its own axis
1.) Effect of Altitude on Acceleration due to Gravity:
Let us consider:
The mass of the earth = $M_{e}$
The radius of the earth = $R_{e}$
A satellite is moving around the earth from the surface of the earth at height= $h$
The gravitational acceleration on the surface of the earth at point $A$
$g=\frac{GM_{e}}{R_{e}^{2}} \qquad (1.1)$
The gravitational acceleration on the altitude $h$ from the surface of the earth at point $B$
$g'=\frac{GM_{e}}{\left( R_{e} + h \right)^{2}} \qquad(1.2)$
Now divide equation $(1.2)$ by equation $(1.1)$
$\frac{g'}{g}= \frac{\frac{GM_{e}}{\left( R_{e} + h \right)^{2}}}{\frac{GM_{e}}{R_{e}^{2}}}$
$\frac{g'}{g}= \frac{R_{e}^{2}}{\left( R_{e} + h \right)^{2}}$
$\frac{g'}{g}= \frac{R_{e}^{2}}{R_{e}^{2} \left( 1 + \frac{h}{R_{e}} \right)^{2}}$
$\frac{g'}{g}= \frac{1}{ \left( 1 + \frac{h}{R_{e}} \right)^{2}}$
$\frac{g'}{g}= \left( 1 + \frac{h}{R_{e}} \right)^{-2}$
Now apply the binomial theorem
$\frac{g'}{g}= 1 - \frac{2h}{R_{e}} + \frac{3h^{2}}{R_{e}^{2}}$
Here $h \lt R_{e}$ then $h^{2} \lt \lt R_{e}^{2}$ so neglect the term of higher power of $\frac{3h^{2}}{R_{e}^{2}}$. Therefore we get
$\frac{g'}{g}= 1 - \frac{2h}{R_{e}} $
$g'= \left( 1 - \frac{2h}{R_{e}} \right) g $
From the above equation it is clear that the value $\left( 1 - \frac{2h}{R_{e}} \right) \lt 1$ then
$g' \lt g$
So, the gravitational acceleration $g$ decreases above the earth's surface.
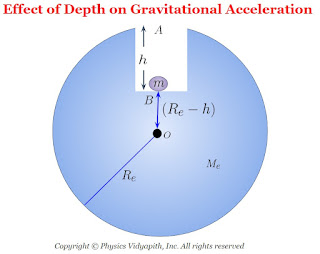
2.) Effect of depth below the earth's surface on Acceleration due to Gravity:
Let us consider:
The mass of the earth = $M_{e}$
The mass of the earth at depth $h$ from the surface of the earth = $M'_{e}$
The radius of the earth = $R_{e}$
The gravitational acceleration on the surface of the earth at point $A$
$g=\frac{GM_{e}}{R_{e}^{2}} \qquad (2.1)$
The gravitational acceleration at point $B$ on the depth $h$ from the surface of the earth
$g'=\frac{GM'_{e}}{\left( R_{e} - h \right)^{2}} \qquad(2.2)$
Now divide equation $(2.2)$ by equation $(2.1)$
$\frac{g'}{g}= \frac{\frac{GM'_{e}}{\left( R_{e} - h \right)^{2}}}{\frac{GM_{e}}{R_{e}^{2}}}$
$\frac{g'}{g}= \frac{R_{e}^{2}}{\left( R_{e} - h \right)^{2}} \left( \frac{M'_{e}}{M_{e}} \right) \qquad(2.3)$
If $\rho$ is the density of the earth the total mass of the earth and the mass of the earth at depth $h$
$M_{e}=\frac{4}{3}\pi R_{e}^{3} \rho$
$M'_{e}=\frac{4}{3}\pi \left ( R_{e}-h\right)^{3} \rho$
Now subtitute the value of $M_{e}$ and $M'_{e}$ in equaion $(2.3)$
$\frac{g'}{g}= \frac{R_{e}^{2}}{\left( R_{e} - h \right)^{2}} \left( \frac{\frac{4}{3}\pi \left ( R_{e}-h\right)^{3} \rho}{\frac{4}{3}\pi R_{e}^{3} \rho} \right) $
$\frac{g'}{g}= \frac{\left( R_{e} - h \right)}{R_{e}}$
$\frac{g'}{g}= \left( 1 - \frac{h}{R_{e}} \right)$
$g'= \left( 1 - \frac{h}{R_{e}} \right)g$
From the above equation it is clear that the value $\left( 1 - \frac{h}{R_{e}} \right) \lt 1$ then
$g' \lt g$
So, the gravitational acceleration $g$ decreases below the earth's surface.
3.) Effect of the shape of the earth:
Earth is not a perfect sphere. It is flattened at the poles and bulges out at the equator. The equatorial radius $R_{E}$ of the earth is about $21 Km$
Then greater than the polar radius $R_{P}$. Now from the equation $g=\frac{GM}{R^{2}}$ $\left (i.e. g \propto \frac{1}{R^{2}} \right)$, we can conclude that the higher radius has less gravitational acceleration because of that the value of $g$ is least at equator and maximum at the pole.
4.) Effect of rotation about its own axis:
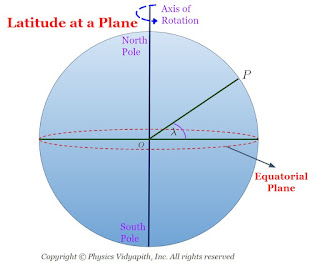
Latitude at a plane is defined as the angle at which the line joining the place to the centre of the earth, makes with the equatorial plane. It is generally denoted by the $\lambda$.
From the figure given below, the latitude at a place $P = \angle OPC = \lambda$
Consider earth is in a perfect sphere of mass $M_{e}$, radius $R_{e}$ with centre $O$. The whole mass of the earth is supposed to be concentrated at the centre $O$. As the earth rotates about its polar axis from west to east, every particle lying on its surface moves along a horizontal circle with the same angular velocity as that of the earth. The centre of each circle lies on the polar axis.
Let us consider, a particle of mass $m$ at a place $P$ of latitude $\lambda$. If the earth is rotating about its polar axis $NS$ with constant angular velocity $\omega$, then the particle also rotates and describes a horizontal circle of radius $r$, Where
$r=PC=OP \: cos\lambda = R \: cos\lambda \qquad (3.1)$
The centrifugal force acting on the particle at $P$ is $m\: r \: \omega^{2}$. It acts along $PA$ directed away from the centre $C$ of the circle of rotation.
The true weight of the particle = $mg$
The centrifugal force at P = $m\: r \: \omega^{2}$
So the resultant of true weight and centrifugal force is $mg'$ can be found by Using the parallelogram law of the forces i.e
$mg'=\sqrt{(mg)^{2}+(mr\omega^{2})^{2}+2(mg)(mr\omega^{2})cos (180^{\circ}- \lambda)}$
$g'=\sqrt{(g)^{2}+(r\omega^{2})^{2}+2(g)(r\omega^{2})cos\lambda)}$
$g'=\sqrt{(g)^{2}+(\omega^{2} R \: cos \lambda )^{2}+2(g)( \omega^{2} R \: cos \lambda )cos\lambda)} \qquad \left( \because r=R \: cos \lambda \right)$
$g'=g \left( 1 + \frac{R^{2}\omega^{4}}{g^{2}} cos^{2} \lambda - \frac{2R \omega^{2}}{g} cos^{2} \lambda)\right)^{\frac{1}{2}}$
Here the value of $\frac{R \omega^{2}}{g}$ is very small, therefore the terms with its squares and of higher power can be neglected. So the above equation can be written as:
$g'=g \left( 1 - \frac{2R \omega^{2}}{g} cos^{2} \lambda)\right)^{\frac{1}{2}}$
Now apply the binomial theorem, and we get
$g'=g \left( 1 - \frac{1}{2}\frac{2R \omega^{2}}{g} cos^{2} \lambda)\right)$
$g'=g \left( 1 - \frac{R \omega^{2}}{g} cos^{2} \lambda)\right)$
$g'= \left( g - R \omega^{2} cos^{2} \lambda\right) \qquad(3.2)$
As, $cos \lambda$ and $\omega$ are positive, therefore $g' \lt g$. Thus from the above equation, it is clear that acceleration due to gravity:
i.) Decreases on account of the rotation of the earth
ii.) Increases with the increase in the latitude of the place.
At equator,
$\lambda = 0^{\circ}$
$g'=p_{e}$
Then from above equation $(3.2)$,
$g_{e}=g-R\omega^{2}$
Clearly, $g_{e}$ is minimum.
At pole,
$\lambda = 90^{\circ}$
$g'=g_{p}$
Then from above equation $(3.2)$,
$g_{p}=g-R\omega^{2 (0)}$
$g_{P}=g$
Clearly, $g_{p}$ is maximum.
Hence, the value of acceleration due to gravity is minimum at the equator and maximum at the poles. The value of acceleration due to gravity at the poles will remain unchanged whether the earth is at rest or rotating.
The difference in the value of acceleration due to gravity at the pole and equator:
We know that:
Acceleration due to gravity at the equator is
$g_{e}=g-R\omega^{2}$
Acceleration due to gravity at the pole is
$g_{p}=g$
The difference in gravitational acceleration at the equator and pole
$g_{p} - g_{e}= g - \left(g-R\: \omega^{2} \right)$
$g_{p} - g_{e}= R\: \omega^{2}$
$g_{p} - g_{e}= R\: \left( \frac{2 \pi }{T}\right)^{2}$
Now put $T=24 \times 60 \times 100$
$g_{p} - g_{e} \approx 0.034 m/sec^{2}$