Derivation of force on current-carrying conductor in uniform magnetic field:
Let us consider:
The length of the conductor - $l$
The cross-section area of the current carrying conductor - $A$
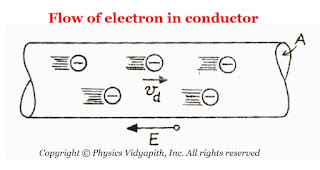
The current flow in a conductor- $i$
The drift or average velocity of the free electrons - $v_{d}$
The current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field - $B$
The total number of free electrons in the current carrying conductor - $N$
Now the magnetic force on one free electron in a conductor -
$F'= ev_{d}B sin\theta \qquad(1)$
The net force on the conductor is due to all the free electrons present in the conductor
$F=N\: F' \qquad(2)$
Let $N$ is the number of free electrons per unit volume of conductor. So the total number of free electrons in the $Al$ volume of the conductor will be
$N=nAl \qquad(3)$
Now substitute the value of $N$ and $F'$ from above equation $(1)$ and equation $(3)$ in equation $(2)$
$F=neAlv_{d}B\: sin\theta$
Where $i=neAv_{d}$
So from the above equation
$F=ilB \: sin\theta $
The Vector Form of the above equation:
$F=i \left(\overrightarrow{l} \times \overrightarrow{B} \right) $
Let us consider, a conductor of length of $l$ in which $i$ current carrying is flowing and placed in magnetic field $B$ at an angle $\theta$. If $i$ current is flowing in the conductor then magnetic force on the conductor depends upon
1) The magnetic force is directly proportional current.
$F \propto i \qquad(1)$
2.) The magnetic force is directly proportional to the length of the conductor.
$F \propto l \qquad(2)$
3.) The magnetic force is directly proportional to the magnetic field.
$F \propto B \qquad(3)$
4.) The magnetic force is directly proportional to the $sin \theta$. Here $\theta$ is the angle between the length of the current element and the magnetic field.
$F \propto sin \theta \qquad(4)$
from equation $(1)$, $(2)$, $(3)$, and equation $(4)$
$F \propto i \: l \: B sin\theta$
$F = k \: i \: l \: B sin\theta$
Here $k$ is constant which has value $1$, then above equation
$F = i\: l \: b \: sin\theta$
Vector form of the above equation:
$F = i \left( \overrightarrow{l} \times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$
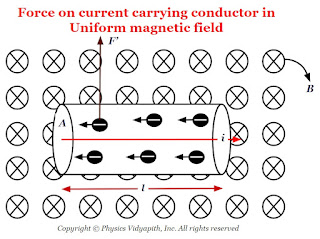 |
| Force on current carrying conductor in the uniform magnetic field |
Alternative Method